四个基本的OS概念
- thread(线程) 一个独立的独一无二的执行过程上下文,完整的描述了一个程序状态
涉及到的部件:program counter,register,execution flags 和stack. - address space 程序在一个地址空间和实际的机器的存储空间区分
- process 一个执行程序的实例化,包含一个地址空间和一些thread.
- Dual mode operation/protection 只有system有能力访问特定的资源 os和hardware 被保护不被user program 修改,user program 彼此isolated,通过控制程序中的虚拟地址空间向物理地址空间的转换.
程序如何跑起来
- load instruction and data segments of executable file into memory
- create stack and heap
- transfer control to program
- Provide services to program
- while protecting OS and program
指令的执行过程
fetch, decode, execute, write, next PC
接下来分别介绍各个概念
thred of control
相关的register保存thread的context, rsp, base pointer, heap pointer,data等 当一个线程驻留在处理器的寄存器上时,它在该寄存器上运行.
一个线程的root state 放在寄存器上,其余放在内存里Program’s address space
the set of accessible addresss and state associate with it. 程序执行时会遇到的段: code segment,包含可执行指令,只读并且定长 Data segment :包含global ,static variable,还有string BSS, 存储unintialized, initialized 0 static Heap malloc stack 存放 autamatic variable 和return address
Multithread of control
illusion of multiple processors: multiplex in time 每个virtual processor 都要维护一定状态: pc, sp, register 如何在virtual CPU之间进行转换: load 和store 怎样触发转换: Timer, voluntary yield, I/O, other
concurrency 所要处理的问题
资源只有一个, hardware, i/o 每个线程都认为他们都对资源有着独一无二的拥有权, 系统需要处理进程,中断,i/o 最终采用vitrual machine abstraction 来进行抽象。
需要为该模型添加protectionprotection
primary mechanism:limit translation from program address space to physical address.
additional Mechanisms:
privileged instructions, inout instructions, special registers syscall processing, subsystem implementaitonthird concept process
execution environment with restricted rights
address space with several threads owns file descriptors, file system contextDual mode operation
hardware 至少提供俩种mode, user mode 和kernel mode hardware如何支持俩种mode:采用一些位的设置, 一些操作或行为只允许发生在kernel mode中,在user mode将导致trap 或者 fail
user 向 kernal 转化 system mode and save PC kernal 向user 转化 user mode restore PC protection的机制: base & bound , translation
protection的机制: base & bound , translation3 types of mode transfer
syscall :
- process request a system device like exit
- like a function call, but out the process
- 没有相关syscall 的地址去调用
- like a remote procedure call
- 将相关参数和syscall id放入register中,去调用相关os Interrupt: 异步的外界的事务触发上下文切换 timer, i/o device 独立于进程 Trap or Exception 在进程内的同步的事务触发上下文切换; segmant fault, divide zero 以上的type统称为unprogrammed control transfer. 如何找到相关的address, 利用interrupt vector, vector中存放对应id的处理函数的地址,中断发生时pc的地址是相关vector 的地址,执行,触发context switch process control block
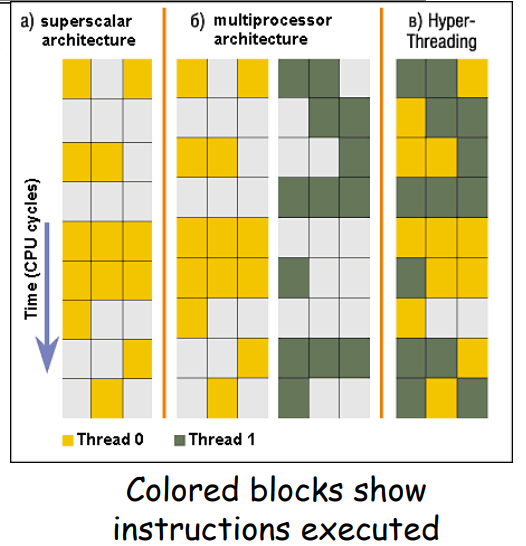
Simultaneous MultiThreading/Hyperthreading
Hardware schedulinb technique
- Superscalar processor can execute multiple insts thar are independent
- Hyperthreading duplicates register state to make a second thread, allowing ore insts to run. Can schedule eack thread as if weew separate CPU.
Branch & Bound 的缺点:
- Inflexible/Wasteful 必须指定特定的物理地址为未来可能的使用,这与stack 和heap 特型不符
- Fragmentation Kernel 不得不将整个process放入到连续的物理内存中 经过一段时间后,memory变得碎片化
- Sharing process之间,process与kernel之间之间分享数据很困难 需要经由kernel进行间接交流
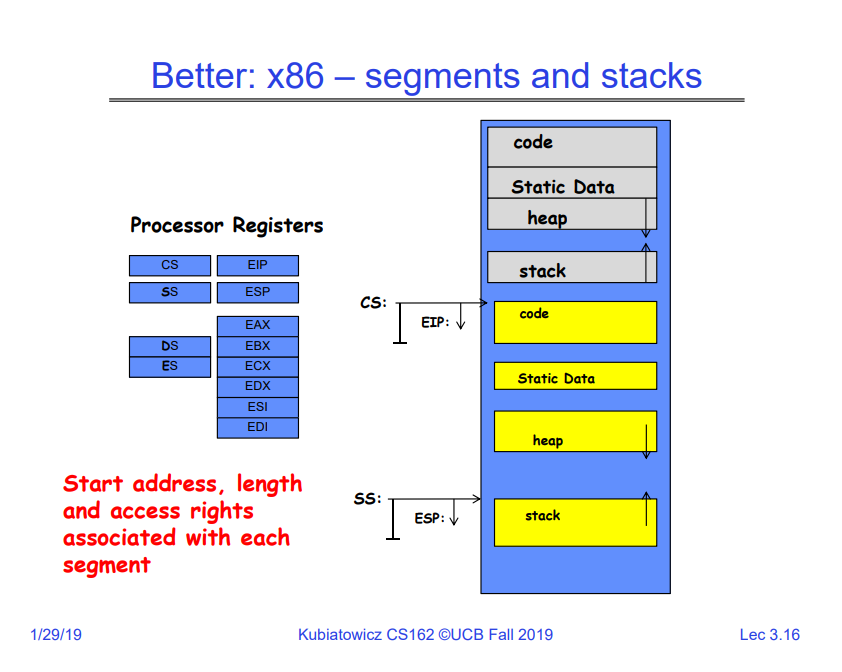
更好的方式: segment and stack
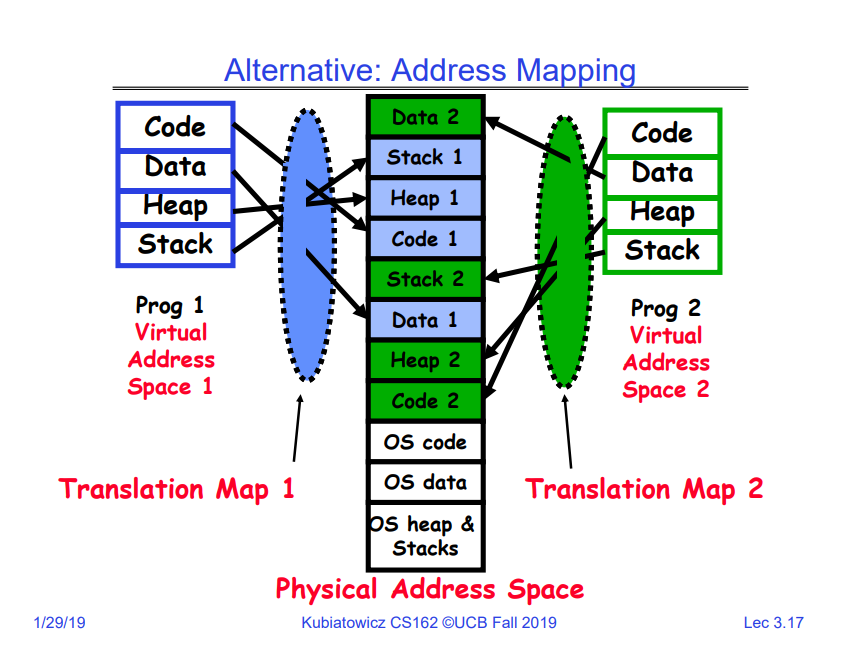
alternative
Implmenting Safe kernel transfer
- important aspects: transfer control to kernel (利用syscall table) separate kernel stack 如何存放相关user process 的信息 如何防止buggy user process ruin kernel
Need for separate kernel stack
- Kernel nedds space to work
- can not put everything on stack
- two stack model: kernel exception stack in kernel space,and user stack in user space Syscall handler copies user args to kernel before invoking specific function
Kernel system call handler
vector through defined syscall entry point locate local arguments: some in reg some in memory copy arguments:
from user mem to kernel mem validate arguments copy result back into user spaceinterrupt control
Interrupt processing non visble to the usr process
- occurs between insts, restarted transparently(注意precise 和imprecise interrupt的区别, 注意在pipeline 和 suprscalar的区别)
- Interrupt handler disables all interrupts, re-enables after completion
- non-blocking, (run to completion)
OS kernel may enable or disable interrupts: x86 CLI, STI 有atomic的操作: 选择下一个thread或者process去执行,或者由syscall,interrupt的返回 interrupt 有优先级, 可以通过mask off 禁止某些 interrupt, 有些interrupt是non maskable-interrupts(NMI:例如segmention fault, 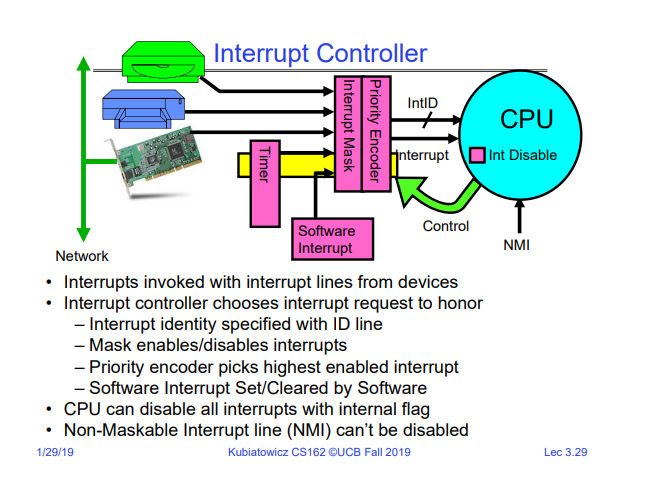 如何安全
如何安全